Hello friends, In this post, I will show how to send mail with GMail using OAuth2.0 in Android. This Project contains a lot of steps like Permission, Google Play Service check to do.
So, please download the project to perform GMail API completely.
First of All, we have to generate OAuth key in Google API Console. To Generate OAuth Key, use your SHA1 key and your app's Package Name as in your Manifest.Paste Following code in your Command Prompt to get SHA1 key in Windows
keytool -list -v -keystore "%USERPROFILE%\.android\debug.keystore" -alias androiddebugkey -storepass android -keypass androidProject Structure
Create a new Project in Android Studio with the required Specifications.AndroidManifest.xml
Don't forget to add the following permission in your manifest file.<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.GET_ACCOUNTS"/>
<!--Added for Accessing External Storage-->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>- mail.jar
- activation.jar
- additionnal.jar
build.gradle
Open your app level build.gradle file add the following lines.dependencies {
compile fileTree(include: ['*.jar'], dir: 'libs')
testCompile 'junit:junit:4.12'
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:23.3.0'
compile 'com.android.support:design:23.3.0'
compile 'com.google.android.gms:play-services-identity:8.4.0'
compile('com.google.api-client:google-api-client-android:1.22.0') {
exclude group: 'org.apache.httpcomponents'
}
compile('com.google.apis:google-api-services-gmail:v1-rev44-1.22.0') {
exclude group: 'org.apache.httpcomponents'
}
compile files('libs/mail.jar')
compile files('libs/activation.jar')
compile files('libs/additionnal.jar')
}GoogleAccountCredential mCredential;
String[] SCOPES = {
GmailScopes.GMAIL_LABELS,
GmailScopes.GMAIL_COMPOSE,
GmailScopes.GMAIL_INSERT,
GmailScopes.GMAIL_MODIFY,
GmailScopes.GMAIL_READONLY,
GmailScopes.MAIL_GOOGLE_COM
};// Initialize credentials and service object.
mCredential = GoogleAccountCredential.usingOAuth2(
getApplicationContext(), Arrays.asList(SCOPES))
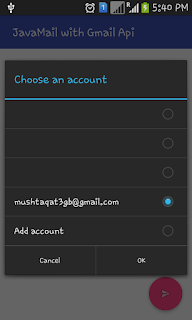
.setBackOff(new ExponentialBackOff());// Start a dialog from which the user can choose an account
startActivityForResult(mCredential.newChooseAccountIntent(), Utils.REQUEST_ACCOUNT_PICKER);// Async Task for sending Mail using GMail OAuth
private class MakeRequestTask extends AsyncTask {
private com.google.api.services.gmail.Gmail mService = null;
private Exception mLastError = null;
private View view = sendFabButton;
public MakeRequestTask(GoogleAccountCredential credential) {
HttpTransport transport = AndroidHttp.newCompatibleTransport();
JsonFactory jsonFactory = JacksonFactory.getDefaultInstance();
mService = new com.google.api.services.gmail.Gmail.Builder(
transport, jsonFactory, credential)
.setApplicationName(getResources().getString(R.string.app_name))
.build();
}
@Override
protected String doInBackground(Void... params) {
try {
return getDataFromApi();
} catch (Exception e) {
mLastError = e;
cancel(true);
return null;
}
}
private String getDataFromApi() throws IOException {
// getting Values for to Address, from Address, Subject and Body
String user = "me";
String to = Utils.getString(edtToAddress);
String from = mCredential.getSelectedAccountName();
String subject = Utils.getString(edtSubject);
String body = Utils.getString(edtMessage);
MimeMessage mimeMessage;
String response = "";
try {
mimeMessage = createEmail(to, from, subject, body);
response = sendMessage(mService, user, mimeMessage);
} catch (MessagingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return response;
}
// Method to send email
private String sendMessage(Gmail service,
String userId,
MimeMessage email)
throws MessagingException, IOException {
Message message = createMessageWithEmail(email);
// GMail's official method to send email with oauth2.0
message = service.users().messages().send(userId, message).execute();
System.out.println("Message id: " + message.getId());
System.out.println(message.toPrettyString());
return message.getId();
}
// Method to create email Params
private MimeMessage createEmail(String to,
String from,
String subject,
String bodyText) throws MessagingException {
Properties props = new Properties();
Session session = Session.getDefaultInstance(props, null);
MimeMessage email = new MimeMessage(session);
InternetAddress tAddress = new InternetAddress(to);
InternetAddress fAddress = new InternetAddress(from);
email.setFrom(fAddress);
email.addRecipient(javax.mail.Message.RecipientType.TO, tAddress);
email.setSubject(subject);
// Create Multipart object and add MimeBodyPart objects to this object
Multipart multipart = new MimeMultipart();
// Changed for adding attachment and text
// This line is used for sending only text messages through mail
// email.setText(bodyText);
BodyPart textBody = new MimeBodyPart();
textBody.setText(bodyText);
multipart.addBodyPart(textBody);
if (!(activity.fileName.equals(""))) {
// Create new MimeBodyPart object and set DataHandler object to this object
MimeBodyPart attachmentBody = new MimeBodyPart();
String filename = activity.fileName; // change accordingly
DataSource source = new FileDataSource(filename);
attachmentBody.setDataHandler(new DataHandler(source));
attachmentBody.setFileName(filename);
multipart.addBodyPart(attachmentBody);
}
// Set the multipart object to the message object
email.setContent(multipart);
return email;
}
private Message createMessageWithEmail(MimeMessage email)
throws MessagingException, IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream bytes = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
email.writeTo(bytes);
String encodedEmail = Base64.encodeBase64URLSafeString(bytes.toByteArray());
Message message = new Message();
message.setRaw(encodedEmail);
return message;
}
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
mProgress.show();
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String output) {
mProgress.hide();
if (output == null || output.length() == 0) {
showMessage(view, "No results returned.");
} else {
showMessage(view, output);
}
}
@Override
protected void onCancelled() {
mProgress.hide();
if (mLastError != null) {
if (mLastError instanceof GooglePlayServicesAvailabilityIOException) {
showGooglePlayServicesAvailabilityErrorDialog(
((GooglePlayServicesAvailabilityIOException) mLastError)
.getConnectionStatusCode());
} else if (mLastError instanceof UserRecoverableAuthIOException) {
startActivityForResult(
((UserRecoverableAuthIOException) mLastError).getIntent(),
Utils.REQUEST_AUTHORIZATION);
} else {
showMessage(view, "The following error occurred:\n" + mLastError.getMessage());
Log.v("Error", mLastError.getMessage());
}
} else {
showMessage(view, "Request Cancelled.");
}
}
} Screens:
Important
You should add the following lines in proguard while releasing your APK-keep class com.google.** 


Komentar
Posting Komentar