With the latest news from Google I/O comes the new and upgraded Firebase. Firebase is a mobile platform that helps you quickly develop high-quality apps, grow your user base, and earn more money. Firebase is made up of complementary features that you can mix-and-match to fit your needs.
Features of Firebase:
Firebase comes with bunch features essential for every android app starting from authentication to hosting the app.
Advantages of using Firebase:Features of Firebase:
Firebase comes with bunch features essential for every android app starting from authentication to hosting the app.
- Super easy and quick to implement.
- No server side configuration needed. No PHP Scripts and No Database Designs.
- Realtime update without using GCM.
- Autoscaling built-in
- Can start for free (only need to start paying once we hit 50 connections)
- Robust APIs for Javascript (including several frameworks like Angular), iOS, and Android
- Built-in support for authentication services like Facebook, Google, and Twitter
- Declarative Security Rules model allows us to enforce read/write privileges and data validation throughout the tree
- Need to build indexes manually
- May need to build “event log” manually as well (in separate sub-tree?)
- Implementation of REST API could be difficult on embedded platforms
- Data validation rules do not support complex objects directly (you’d need to validate individual child nodes separately)
Setting up Firebase Project:
In this post, I explained how to setup firebase for your Android Project. This method is common for all type of services offered by Firebase such as User Authentication, Realtime Database, Cloud Messaging and so on. Do the following steps for setting up your project and it is common for all services in firebase.
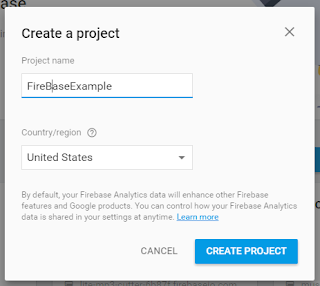
- First thing you need to do is go to https://firebase.google.com/ and make an account to gain access to their console. After you gain access to the console you can start by creating your first project.
- Give the package name of your project (for example FirebaseSample) in which you are going to integrate the Firebase. It redirects to Firebase Dashboard.
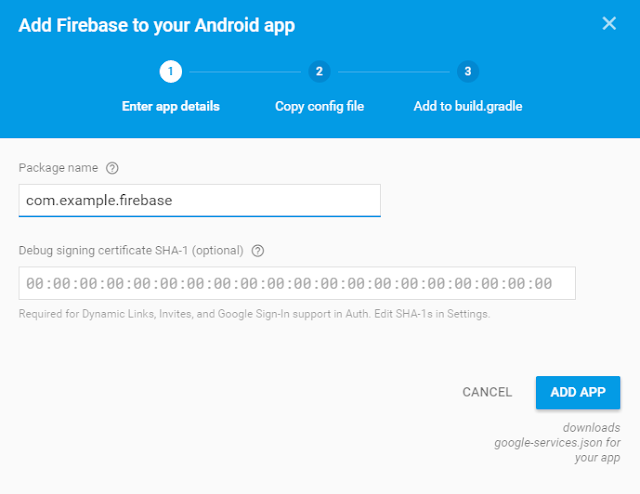
- Here, you select your project type and Here I selected Android Project.
- Then paste your package name as in your manifest file.(com.example.firebase).
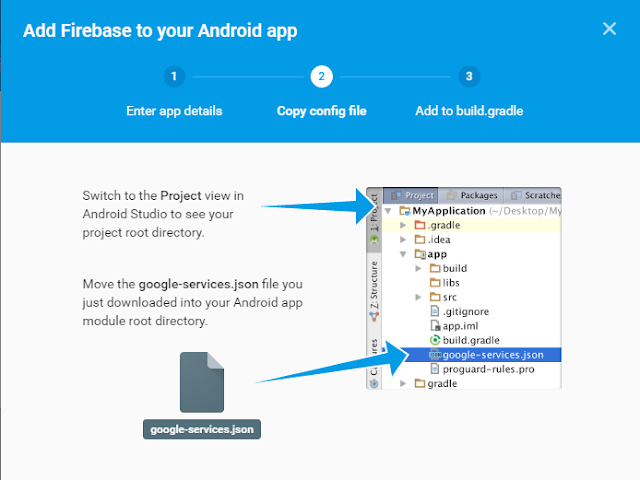
- Now the google-services.json file will be downloaded when you press add app button
- Add this file to your app folder of your Project.



Komentar
Posting Komentar